Exhaust gas heat exchangers operate on a simple term by using the waste heat that’s generated from flue gases during energy generation. The exchanger works just like any normal HVR system in a way that uses the exhaust gas generated by adding it to a second medium, which in most cases is eighter heating water or hot air. Through this principle of work, the existing residual heat can be significantly reduced since it being recovered.
This technology greatly increases the efficiency of an industrial complex by saving on energy and reduction of CO2 emissions. This technology is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
An exhaust gas heat exchanger (EGHE) achieves the similar, if not better, results by utilizing only a simple fraction of the cost. Since it uses lost heat to preheat or keep warm tools, molds, and spaces, it saves the manufacturer a lot of money by recycling the air that would otherwise be considered lost to the environment.
What Are the Applications for EGHE’s? 
Energy prices rise by the day. And that is making energy gas heat exchangers a hot property nowadays. Since they are cost-effective tools that use recycled gas for the purpose of heating or preheating, creating something out of nothing is particularly attractive in the industry.
But yet another thing that EGHE’s do is reduce the C02 emission into the atmosphere. Since the gases are recycled, dangerous and toxic pollutants are also being recycled accordingly, says Exodraft.
The reduction of C02 emissions is very important to energy-intensive industries.
An EGHE can be used wherever there is waste heat generated at the expense of flue gases. The most common cases are bakeries. Hardening plants, plastic processing plants, etc.
Since modern manufacturing processes cannot work without the use of intense temperatures, these industries can greatly benefit by using the same waste heat that they generate, to generate additional energy. To put it simple, they put the waste heat to use by generating additional, free, energy from it.
Modern exhaust gas heat exchangers can reuse up to 96% of the generated waste heat from flue gases. Before that, all of it would go to the atmosphere, completely throwing away the benefits from it. By putting exhaust gases to use, you are effectively increasing the effectiveness and economy of your entire production operation. These are some of the benefits that make exhaust gas heat exchangers particularly a hot topic nowadays, and it’s exactly why more and more manufacturers are choosing to buy into it.
How Does it Work?
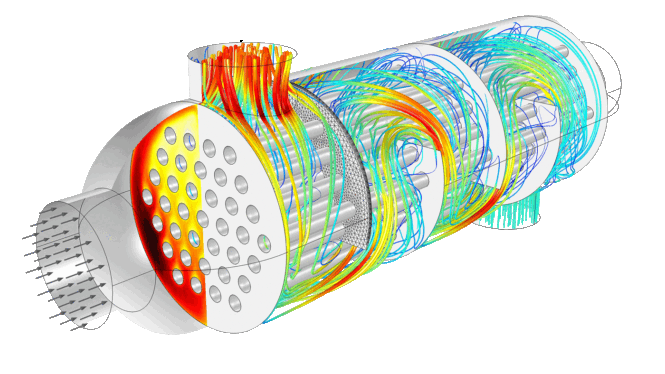
While we did and touch on how an EGHE works, we are going to try and touch on a more complex base.
Every heating system produces waste heat from flue gases. That waste heat is then thrown out into the atmosphere in the form of exhaust gases. An EGHE works by using the waste heat into your advantage. It uses the waste heat, the exhaust gases, to heat the heating medium, which essentially generates energy at the expense of nothing.
To perform this, an EGHE is usually installed between the boiler and chimney, or anything similar. This way there is no need to dismantle eighter of those, saving you time and money in the process. Installation is simple, operating is simple, and the benefits are huge.
 Imagup General Magazine 2024
Imagup General Magazine 2024



